The Science Behind Silicone Gel in Wound Healing: Unveiling Its Moisture-Locking Power
Jun 04, 2025

Wound care is essential for managing chronic and complex wounds, such as pressure ulcers, incontinence-associated dermatitis (IAD), and scars. Nonhealing wounds are often characterized by poor epidermal migration. Silicone gel has emerged as a versatile and effective solution for these challenges, primarily due to its ability to create an optimal healing environment by regulating moisture and providing protection. This makes it a valuable tool for both healthcare professionals and patients.
Mechanisms of Silicone Gel in Wound Healing
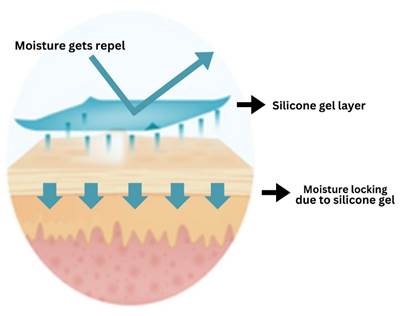
Silicone gel supports the healing process in several ways, primarily through the following mechanisms:
-
Hydration and Moisture Regulation
A primary function of silicone gel is its ability to regulate moisture at the wound site. It forms a semi-occlusive layer that mimics the skin’s natural barrier, preventing excessive trans epidermal water loss (TEWL). This moisture balance is critical for wounds like pressure ulcers and IAD, which are vulnerable to damage from prolonged pressure or moisture exposure.
Silicone gels are known for their low Water Vapor Transmission Rate (WVTR), which measures the amount of moisture that passes through a material over time. The low WVTR of silicone gel ensures that moisture is locked in, creating a conducive environment for healing. This facilitates cellular processes such as fibroblast activity, collagen synthesis, and re-epithelialization, all of which are vital for wound healing.
-
Protection Against External Contaminants
In addition to moisture regulation, silicone gel acts as a protective barrier, shielding wounds from bacteria, pathogens, and other external contaminants. This is particularly crucial for wounds prone to infection, such as pressure ulcers and IAD. For IAD, where the skin frequently faces irritants like urine or feces, silicone gel provides a protective layer that minimizes the risk of further breakdown. By reducing the likelihood of infection and irritation, silicone gel allows the body’s natural healing processes to function effectively. -
Modulation of Electrical Charges and Cellular Activity
Silicone gel promotes wound healing by facilitating epidermal migration through the modulation of electrical charges. This unique property, combined with its bacteriostatic effects, helps create a conducive healing environment. Furthermore, silicone gel regulates critical biological processes in wound healing. Chronic wounds often show imbalances in growth factors that impede healing. Silicone gel helps modulate key growth factors, such as fibroblast growth factor β (FGF β) and transforming growth factor β (TGF β), which are involved in cellular proliferation and collagen synthesis. TGF β stimulates collagen production, essential for healing, while FGF β enhances cellular activity, aiding in wound remodeling and preventing excessive scarring.
Broader Applications of Silicone Gel in Wound Care Beyond managing pressure ulcers and IAD, silicone gel has broader applications in treating surgical wounds, traumatic injuries, and burns:
-
Surgical Wounds and Traumatic Injuries: Silicone gel is often used postoperatively to manage incisions and reduce the risk of hypertrophic scarring, thereby improving cosmetic and healing outcomes.
-
Burns: In burn care, silicone gel helps maintain moisture balance, reducing pain and preventing infection while supporting skin regeneration.
It's time to embrace a transformative approach to wound care—one where the benefits of silicone gel are recognized and harnessed to create optimal healing environments for everyone. By prioritizing moisture regulation, infection protection, and balanced cellular activity, we can empower individuals to take charge of their healing journeys, unlocking the full potential of the body’s natural recovery processes.
