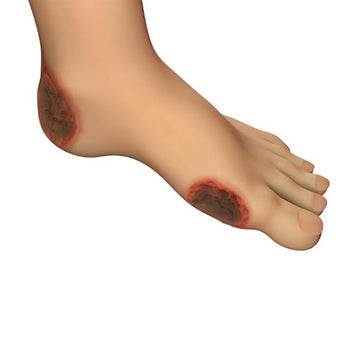
What are Foot Ulcers?
Foot ulcers are open sores or lesions that develop on the foot and typically take a long time to heal. They most commonly occur on the bottom of the foot, especially the heel and ball of the foot.
Foot ulcers can be caused by a number of conditions, but the most common cause is diabetes.
Other conditions that can cause foot ulcers include poor circulation, which can also be caused by diabetes; peripheral artery disease (PAD); rheumatoid arthritis; and infections.
Foot ulcers are a serious complication that can lead to infection, gangrene, and even amputation. If you have diabetes or any other condition that increases your risk of foot ulcers, it is important to inspect your feet daily for any cuts, sores, or redness.
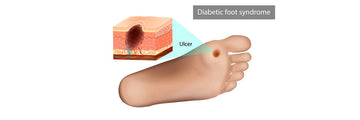
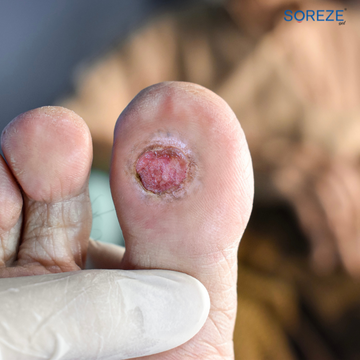
What are Diabetic Foot Ulcers?
Diabetic foot ulcers are open sores on the feet of people with diabetes, caused by factors like poor circulation and nerve damage. They often start from small injuries that go unnoticed due to reduced sensation in the feet. Without proper care, these can lead to infections and serious complications, including amputation. Prevention involves regular foot checks, controlling blood sugar, and wearing proper footwear. Treatment includes wound cleaning, infection management, and improving circulation for healing.